Ppe-Xap: Bacterial Spot Resistance
Bacterial spot, caused by Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni is a serious disease of peach that causes premature defoliation, weak vigor, unmarketable fruit, and decline in yield. Effective control methods are lacking; anti-bacterial sprays are only partially effective and their use is controversial. Incorporating genetic sources of bacterial spot resistance into new cultivars is a more promising control measure. Progress has been made in developing resistant cultivars, yet few such resistant cultivars have achieved commercial success because of the difficulties in combining bacterial spot resistance with high fruit quality.
Genetics
Bacterial spot resistance is quantitative in nature, and there is a high level of variation in susceptibility. A single genomic region on chromosome 6 was found to account for up to 35% of the observed phenotypic variation for fruit bacterial spot resistance. The Ppe-Xap DNA test was developed to target both loci in a single assay to maximize the ability to identify resistant germplasm.
Predictive Capacity
This DNA test explains ~35% of observed phenotypic variation in resistance to fruit bacterial spot disease in U.S. breeding germplasm. By crossing and selecting for specific allelic combinations, you can directly target durable resistance coupled with high fruit quality. The predictive power of Ppe-Xap was confirmed in the RosBREED project on four U.S. peach breeding programs. Confirm the effects in your own germplasm before widespread application.
When to Assay
Ppe-Xap has a range of breeding uses, such as:
- Parent pool selection, to identify parents carrying one, or preferably two, R alleles at each locus.
- Cross choices, to help choose parental combinations that will most effectively provide R-alleles at each locus as well as impart superior fruit quality.
- Seedling selection, to cull susceptible seedlings and only advance those expected to confer durable resistance.
Allelic State of Several Peach Cultivars
| Genotype | Example Cultivars | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|
| S | S & S | S | O’Henry | Very susceptible |
| S | R & R | R | Clayton | Resistant |
| R | R & R | R | White County | Very resistant |
A table of haplotypes for important U.S. peach germplasm can be downloaded here.
Allele Frequency in Elite U.S. Peach Germplasm


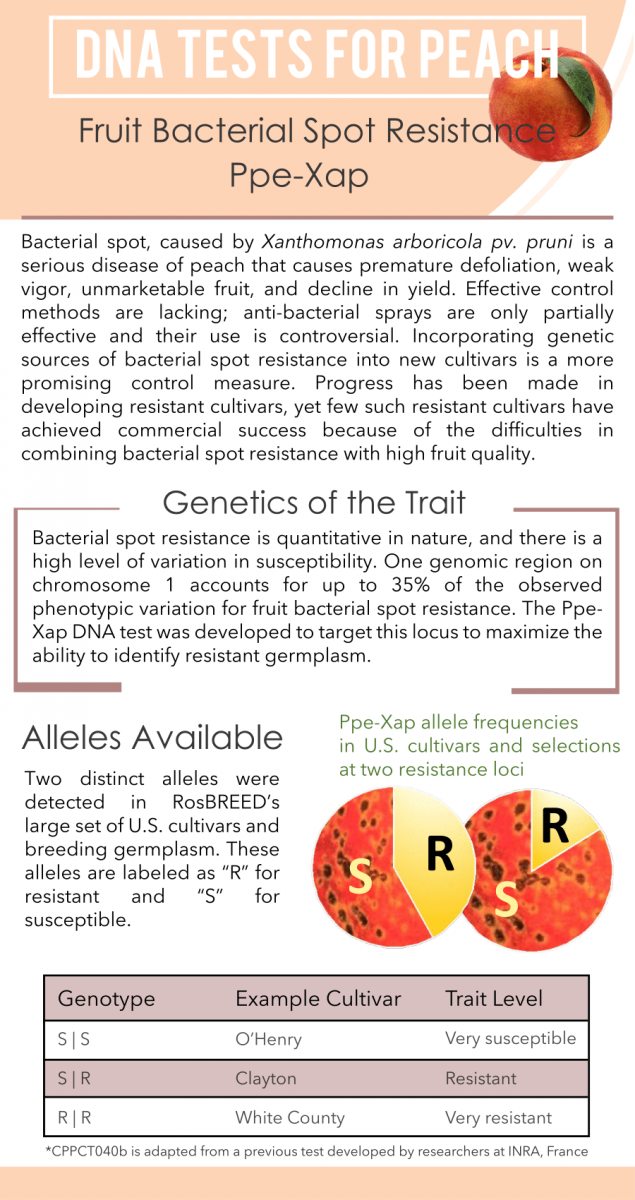
Alleles Available
Two distinct alleles were detected in RosBREED’s large set of U.S. cultivars and breeding germplasm. These alleles are labeled as “R” for resistant and “S” for susceptible.
Technical Details
Ppe-Xap is a simple PCR-based test consisting of four primer pairs multiplexed into a single assay.