G4Mat: Peach Maturity Date
To peach growers, one of the most important characteristics of a particular cultivar is its maturity time, with the most successful new cultivars filling gaps in the harvest season. Therefore, breeders must consider the season of maturity when planning crosses, selecting seedlings, and advancing elite cultivar candidates.
Genetics
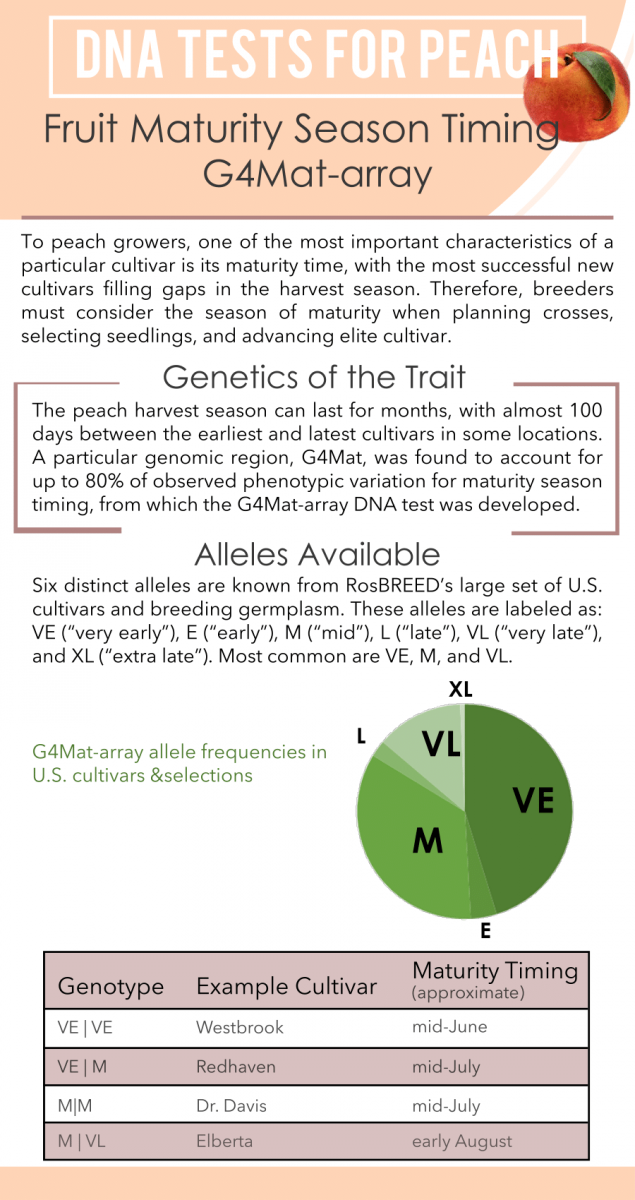
The peach harvest season can last for months, with almost 100 days between the earliest and latest cultivars in some locations. A particular genomic region, G4Mat, was found to account for up to 80% of observed phenotypic variation for maturity season timing, from which the G4Mat DNA test was developed. Six distinct alleles are known from RosBREED’s large set of U.S. cultivars and breeding germplasm. These alleles are labeled as: VE (“very early”), E (“early”), M (“mid”), L (“late”), VL (“very late”), and XL. (“extra late”). Most common are VE, M, and VL.
Predicted Maturity Dates for Some Allelic Combinations
Alleles Available
FaOMT-SI/NO produces two main functional alleles. The dominant + allele is the “turned on” variant. When the - “turned off” allele is homozygous, mesifurane is not found within the berry.
Technical Details
G4Mat-array relies on SNP array genotyping with a custom 24-SNP mini-array or 9K array. Four adjacent SNPs define the locus.
Allelic State of Several Peach Cultivars
| Genotype | Example Cultivars | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|
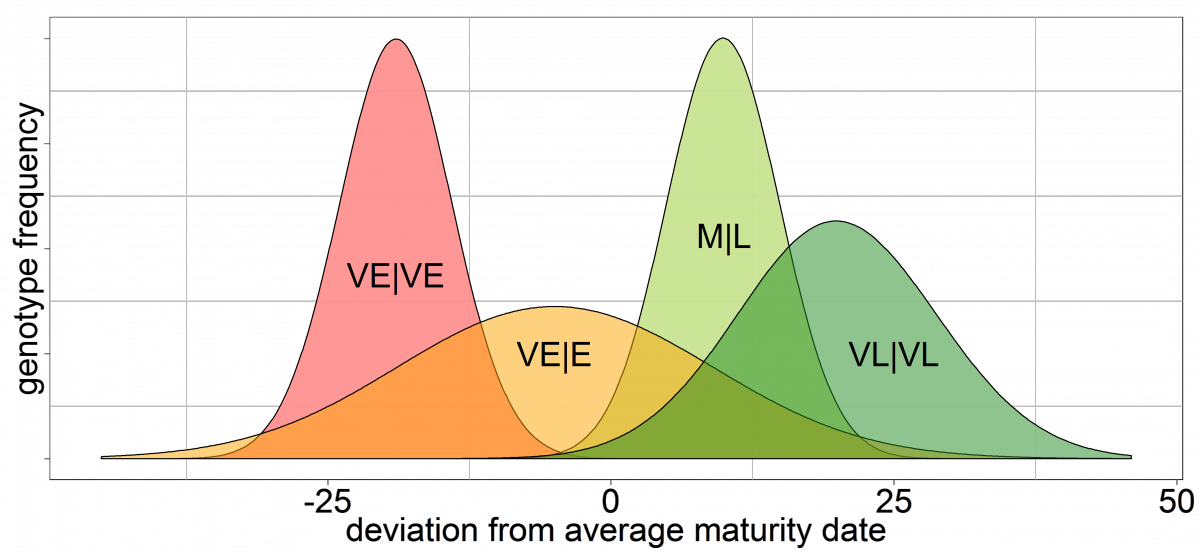
| VE | VE | Westbrook | mid-June |
| VE | M | Redheaven | mid-July |
| M | M | Dr. Davis | mid-July |
| M | VL | Elberta | early August |
A table of haplotypes for important U.S. peach germplasm can be downloaded here.
Predictive Capacity
This DNA test explains almost all of the genetic effects on maturity season timing in U.S. breeding germplasm. By targeting and selecting specific allelic combinations, you can directly focus on one or more desired harvest windows. The predictive power of G4Mat was confirmed in the RosBREED project on four U.S. peach breeding programs. Confirm the effects in your own germplasm before widespread use.
When to Assay
G4Mat has a range of breeding uses, such as:
- Cross choices, to help pick combinations of parents that will produce progeny in specific harvest windows.
- Seedling sorting, to enable planting of groups of seedlings ordered by predicted harvest date.
- Seedling selection, to discard unwanted types and field-plant only those seedlings expected to fruit within a specific harvest window.
G4Mat is a simple PCR-based DNA test that consists of three primer pairs multiplexed into a single assay.